Trust-based collaborative filtering: tackling the cold start problem using regular equivalence
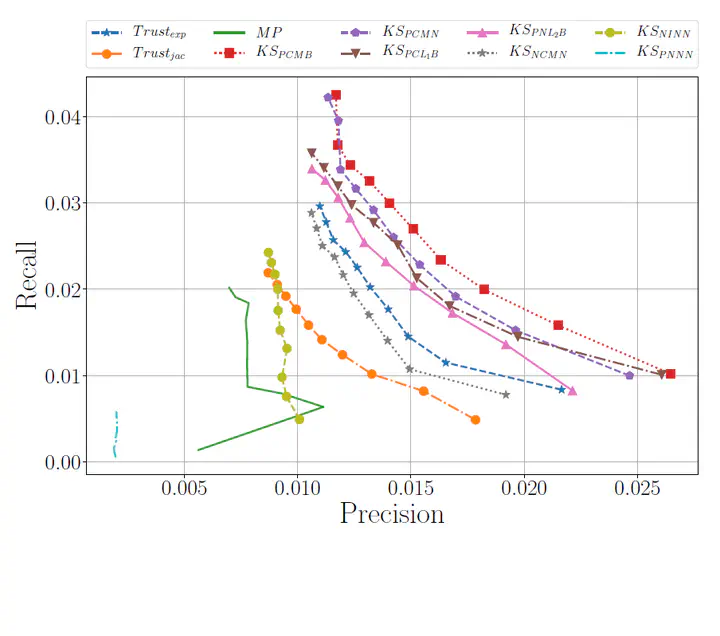 Comparison of recommendation accuracy showing our KSPCMB approach outperforms baseline methods and other KS-based algorithms for cold-start users on the Epinions dataset, with Recall-Precision metrics for various recommendation list sizes.
Comparison of recommendation accuracy showing our KSPCMB approach outperforms baseline methods and other KS-based algorithms for cold-start users on the Epinions dataset, with Recall-Precision metrics for various recommendation list sizes.
Abstract
User-based Collaborative Filtering (CF) is one of the most popular approaches to create recommender systems. This approach is based on finding the most relevant k users from whose rating history we can extract items to recommend. CF, however, suffers from data sparsity and the cold-start problem since users often rate only a small fraction of available items. One solution is to incorporate additional information into the recommendation process such as explicit trust scores that are assigned by users to others or implicit trust relationships that result from social connections between users. Such relationships typically form a very sparse trust network, which can be utilized to generate recommendations for users based on people they trust. In our work, we explore the use of regular equivalence applied to a trust network to generate a similarity matrix that is used to select the k-nearest neighbors for recommending items. We evaluate our approach on Epinions and we find that we can outperform related methods for tackling cold-start users in terms of recommendation accuracy.